DrawingML Shapes
Paragraphs in shapes can have bullets and numbering/lettering applied either by using list styles or with direct formatting within the <a:pPr> element for the paragraph (<a:p>). This page covers the individual properties related to bulleted and numbered/lettered paragraphs. Each of these my be specified as part of a list style. For the definition and application of list styles, see List Properties.
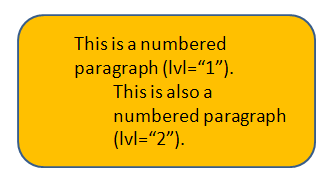
Bullets and numbering are specified using attributes and child elements of <a:pPr>. However, both are affected by the level specified for the paragraph by the lvl attribute on <a:pPr>. The level is specified as a numeric value of between 0 and 8, since there are 9 possible levels defined. For example, <a:pPr lvl="1"/> indicates that the paragraph is a level 2 and should use the lvl2pPr list style as defined within <a:txBody>. See List Properties. Below is a sample shape with two paragraphs--the first specified as level 2 (<a:pPr lvl="1"/>) and the second specified as level 3 (<a:pPr lvl="2"/>). This is before any numbering or bullets have been specified.
Bullets
Images as Bullets
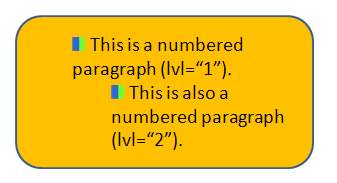
Bullets can be either characters or images. The <a:buBlip> element is used to specifiy an image as a bullet. This element contains a single <a:blip> element which references the image with the value of the r:embed attribute. (For more on blips, see the Overview on pictures, and the related pages.) For example, below is the same shape as above, but with a simple image being used as a bullet for the paragraphs within the shape. The <r:embed="rId2"/> references a <Relationship> in the .rels file for the presentation slide, which has a type of "http://schemas.opemxmlformats.org/officeDocument/2006/relationships.image" and a target of "../media/image1.gif" referencing the image file within the package.
Characters as Bullets
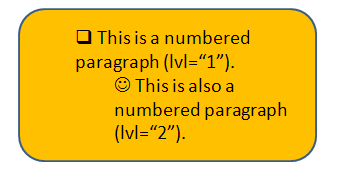
Characters are specified as bullets with the <a:buChar> element. The character can be any character in any font that the system supports, and it is specified in the char attribute of <a:buChar>. The character refers to a character in the font specified by the <a:buFont> element, which is a child of <a:pPr>. The <a:buFont> element specifies a typeface that is registered with the application. The font will only apply to the bullet--not to the text that follows. The typeface is specified in the typeface attribute as a string (e.g., Arial); if the font is not available, font substitution will be performed. There are also charset and pitchFamily attributes. These are not discussed further here. To set the font of the bullet to be the same as the text run that contains the bullet, specify the empty element . The <a:buFontTx>.
Bullet Character Color
The color of bullet characters can be specified with the <a:buClr> element. As with other color within shapes, color is specified as a child element (in this context, a child of <a:buClr>) using one of the following color options: as a preset color (<a:prstClr>), using hue, saturation and luminance (<a:hslClr>), scheme colors (<a:schemeClr>), system colors (<a:sysClr>), or as RGB percentages or hex numbers (<a:scrgbClr> or <a:srgbClr>). Note that these elements corresponding to color specification methods can also have child elements which transform the base color. So, for example, a scheme or theme color may be specified as accent6, but a luminance modulation can also be applied to that base color. Colors are not covered in detail here.
Below is the same shape as above, with the same characters as bullets, but with a color applied to the first bullet.
It is possible to set the color of the bullet to be the same color as the text run that contains the bullet. This is specified with the empty <a:buClrTx> element. Of course if no color is specified for the run, then the color of the bullet will follow the default text color.
Bullet Size
The size of bullet characters can be specified as either a percentage of the surrounding text or in points. A percentage is specified with <a:buSzPct> element. The actual value is specified with the val attribute and must be between 25% and 400%. A size in points is specified with the <a:buSzPts> element. Again the actual value is specified with the val attribute, with 100 being one point size. Below is the same shape as above, except that the first bullet character is set to 350% of the surrounding text.

It is possible to set the bullet size to be the same point size as the text run that contains the bullet. This is specified with the empty <a:buSzTx> element. Of course if no size is specified for the run, then the size of the bullet will follow the default text size.
No Bullets/h3>
To specify that a paragraph within a shape is to have no bullet formatting applied, specify the empty <a:buNone> element as a child of <a:pPr>.
Automatic Numbering
Automatic numbering of paragraphs can be specified with the <a:buAutoNum> element within <a:pPr>. The numbering scheme to be used and the indentation and other characteristics are affected by the attributes of <a:buAutoNum> as well as by the level specified for the paragraph, as discussed above. The auto numbering element has two attributes: startAt and type. The startAt specifies the number that starts the numbering sequence. When the numbering is alphabetical, the number should map to the approprirate latter--e.g., 2 to 'b', 27 to 'aa', etc. The type specifies the numbering scheme to be used. Possible values include:
- alphaLcParenBoth -- (a), (b), (c), ...
- alphaLcParenR -- a), b), c), ...
- alphaLcPeriod -- a., b., c., ...
- alphaUcParenBoth -- (A), (B), (C), ...
- alphaUcParenR -- A), B), C), ...
- alphaUcPeriod -- A., B., C., ...
- arabicParenBoth -- (1), (2), (3), ...
- arabicParenR -- 1), 2), 3), ...
- arabicPeriod -- 1., 2., 3., ...
- arabicPlain -- 1, 2, 3, ...
- romanLcParenBoth -- (i), (ii), (iii), ...
- romanLcParenR -- i), ii), iii), ...
- romanLcPeriod -- i., ii., iii., ...
- romanUcParenBoth -- (I), (II), (III), ...
- romanUcParenR -- I), II), III), ...
- romanUcPeriod -- I., II., III., ...
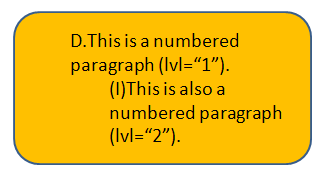
Below is the same shape as above, but with auto numbering set for both paragraphs. The first starts at D, using the alphaUcPeriod scheme, and the second starts at I using the romanUcParenBoth scheme.