DrawingML Shapes
The run-level properties of text within a shape are specified with child elements and attributes of the <a:rPr> element, which is a child element of the <a:r> element. It is important to be mindful that run properties within a shape are frequently not specified in the same way as run properties within wordprocessingML documents. For example, in wordprocessingML documents, properties such as italics and font size are specified as child elements of the run element, whereas in shapes, they are specified as attributes of the run element.
Colors/Fills, Highlight, and Outline
Fills of various kinds can be applied to runs of text. Most commonly, solid fills will be applied to color the text as shown in the example below. The fills are specified as child elements of <a:rPr>, using the same child elements as are used for the fills applied to entire shapes. For more on how to specify the various fill types, see Shape Fill.

Highlight can be specified with the child element <a:highlight> of <a:rPr>. Within the <a:highlight> element is a color specification. Colors can be specified using one of the following color options: as a preset color (<a:prstClr>), using hue, saturation and luminance (<a:hslClr>), scheme colors (<a:schemeClr>), system colors (<a:sysClr>), or as RGB percentages or hex numbers (<a:scrgbClr> or <a:srgbClr>). Note that these elements corresponding to color specification methods can also have child elements which transform the base color. Below is a sample yellow highlight.

An outline style can be specified for a run with the <a:ln> element, a child of <a:rPr>. Various kinds of dash styles, colors, ends, etc. can be specified with attributes and child elements on <a:ln>. For more on outlines, see the page on outlines of shapes.

Bold, Italics, Strike, Underline, Size, and Capitalization
Many of the more common run properties are specified with attributes on <a:rPr>.
| Attribute | Description |
|---|---|
| b | Specifies that the text of the text run is to be bold: b="1". |
| i | Specifies that the text of the text run is to be italics: i="1". |
| cap | Specifies a type of capitalization. The type is determined by the value of the attribute. Note that this does not change the actual characters stored, only the rendering. Possible values are:
|
| sz | Specifies the size of the text: sz="1200". Whole points are specified in increments of 100. A font point size of 12 would be 1200. |
| strike | Specifies that the text of the text run should be formatted as strikethrough text. Possible values are:
|
| u | Specifies that the text of the text run should be underlines. Possible values are:
There are also child elements of <a:rPr> that can affect underline. See below. |
Below is an example of a run that is bold, italics, single underlined, with double strikethrough, and in 24 point.

There are child elements of <a:rPr> that can affect underline. For example, an underline fill can be specified using <a:uFill>. The usual fill types within <a:uFill> can be specified. See Shape Fill. So, for example, if you want the underline to be colored, you can specify a solid fill as shown below.

To specify that the fill color of the underline should be the same color as the text, specifiy <a:uFillTx> as a child of <a:rPr>. To specify that the style of an underline should follow the text, specify <a:uLnTx>
Spacing, Superscript/Subscript, Kerning, Fonts
Spacing between characters within a run is specified with the spc attribute on <a:rPr>. Values are in points, with 100 being 1 point, and 1200 being 12 points. Below is a sample with spacing of the first sentence set to 12 points: <a:rPr lan="en-US" sz="1200" spc="1200">.

Kerning, or the adjustment of spacing between characters in a propertional font, can be specified with the kern attribute on <a:rPr>. The attribute value specifies the minimum font size at which kerning occurs for the run, so values are in points.
Superscripts and subscripts are specified with the baseline attribute on <a:rPr>. Values are in percentages, with a positive value indicating a superscript and a negative value indicating a subscript. Below is an example of a subscript on the word 'Love' (<a:rPr lan="en-US" sz="1200" baseline="-40000">) and a superscript on the word 'striking' (<a:rPr lan="en-US" sz="1200" baseline="30000">).

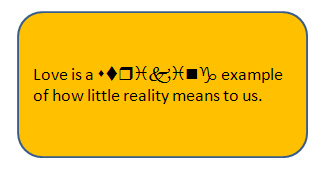
Fonts (Latin-based) can be specified for a run with the <a:latin> child element of <a:rPr>. A typeface attribute specifies the name of the font. Below is a shape with a run of the Wingding typeface.
Links
Hyperlinks within text in a shape are inserted with the <a:hlinkClick> child element of <a:rPr>. The id attribute specifies the relationship id which contains the target for the link. So, for example, <a:hlinkClick r:id="rId2"/> references the relationship in the .rels file for the slide (slide1.xml.rels) that has the id of rId2. That relationship looks like this:
